SETTING AND TRACKING YOUR PAH PATIENT GOALS
The 2022 ESC/ERS Guidelines recommend follow-up assessments every 3 to 6 months for stable patients with PAH.2 Since PAH can progress rapidly, it is critical to monitor your patients often.3
ERS=European Respiratory Society; ESC=European Society of Cardiology; PAH=pulmonary arterial hypertension; WHO=World Health Organization.
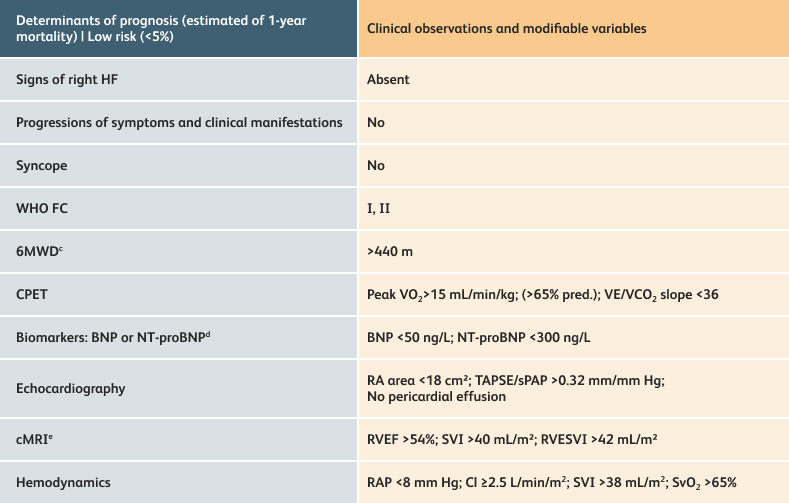

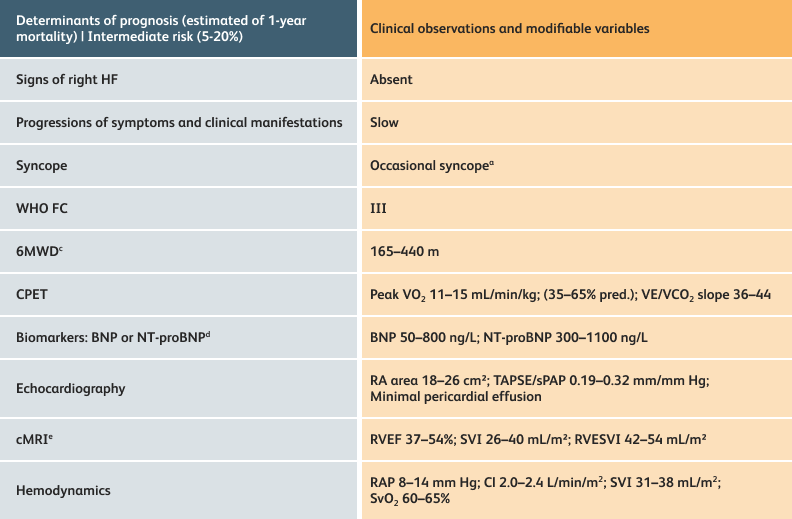
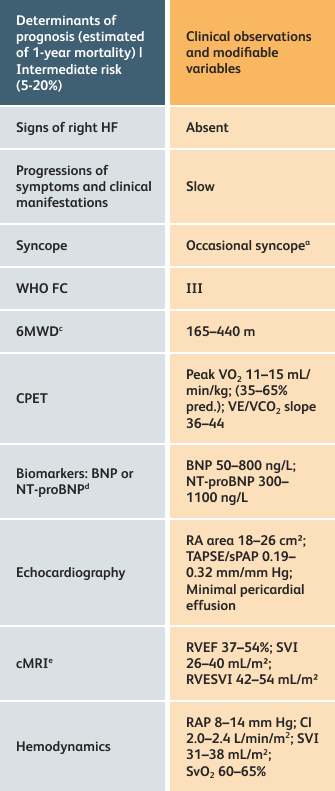
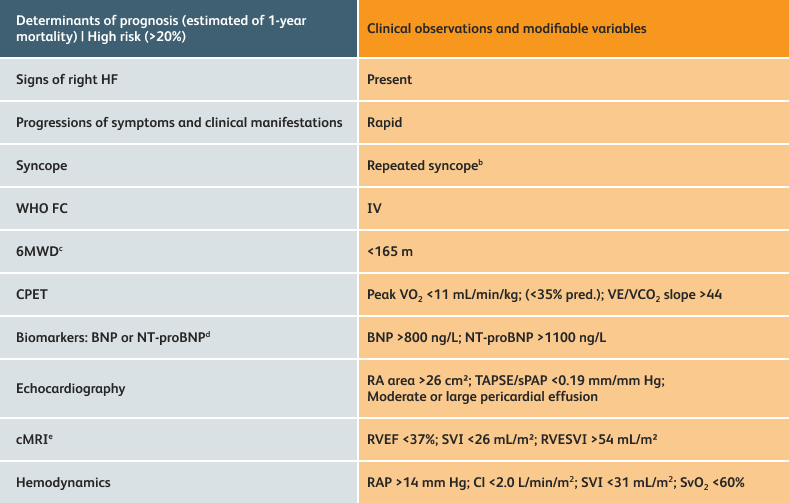
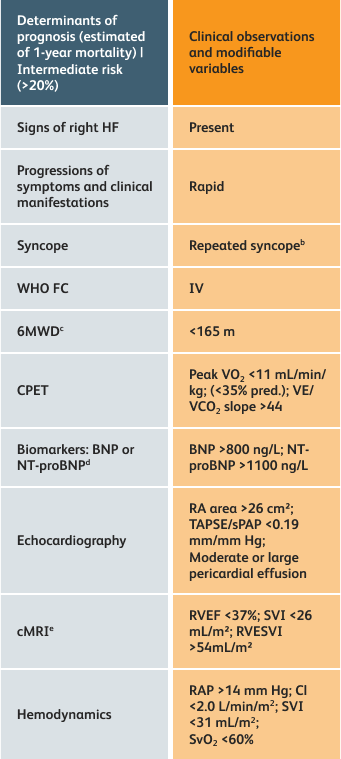
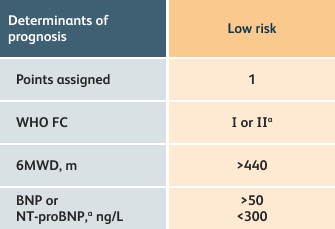
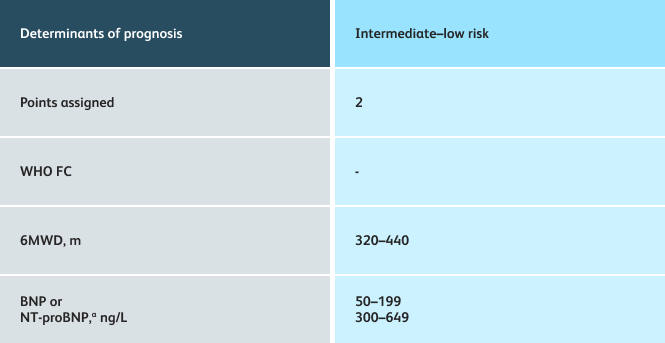
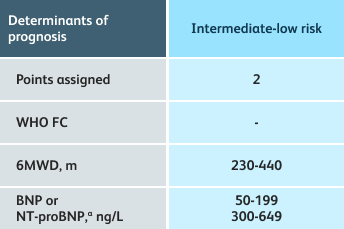
The guidelines above can assist with:
- Creating goals and monitoring progress to help guide the course of treatment
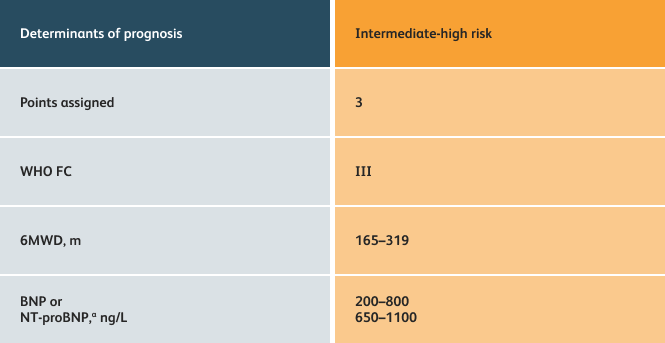
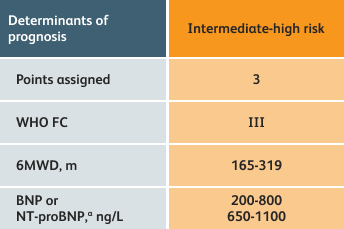
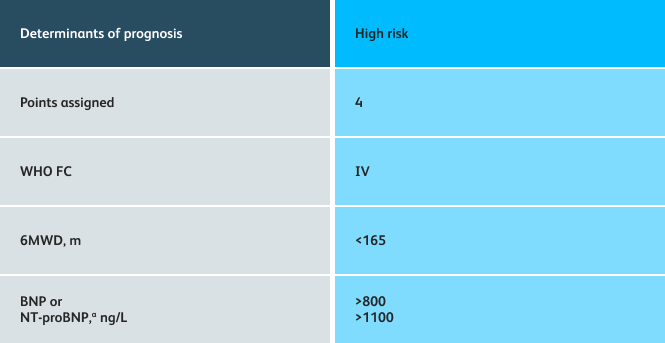
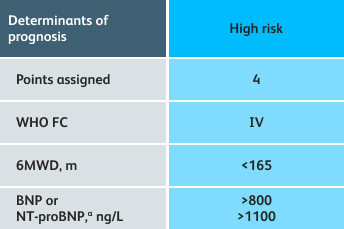
- Setting goals for your PAH patients that include exercise capacity (6MWD), WHO functional class, and hemodynamics
6MWD=6-minute walk distance;
BNP=brain natriuretic peptide;
CI=cardiac index;
cMRI=cardiac magnetic resonance imaging;
CPET=cardiopulmonary exercise testing;
HF=heart failure;
NT-proBNP=N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide;
PAH=pulmonary arterial hypertension; pred.=predicted;
RA=right atrium;RAP=right atrial pressure;
RVEF=right ventricular ejection fraction;
RVESVI=right ventricular end-systolic volume index;
sPAP=systolic pulmonary arterial pressure;
SVI=stroke volume index;
SvO2=mixed venous oxygen saturation;
TAPSE=tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion;
VE/VCO2=ventilatory equivalents for carbon dioxide;
VO2=oxygen consumption;
WHO FC=World Health Organization Functional Class.


CLINICAL DEFINITION
PAH is defined as a mean pulmonary artery pressure (mPAP) >25 mm Hg with a pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (PCWP) ≤15 mm Hg measured by cardiac catheterization.3

TREATMENT LANDSCAPE
The REVEAL Registry evaluated 2525 patients, of whom 2438 were on PAH treatment with ERAs, PCAs, or PDE-5 inhibitors. More than 50% of these patients remained in WHO functional class III or IV.4
CTEPH=chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension; ERA=endothelin receptor antagonist; PCA=prostacyclin analog; PDE-5=phosphodiesterase type 5; V/Q=ventilation/perfusion.
WHO GROUP CLASSIFICATION1,2,6
Identify which WHO group your PH patients are in.
I. PAH
II. PH associated with left heart disease
III. PH associated with lung disease and/or hypoxia
IV.I CTEPH
V. PH with unclear and/or multifactorial mechanism
Adempas is approved for adults with PAH (WHO Group 1) and inoperable or persistent/recurrent CTEPH (WHO Group 4) after surgery. Adempas has been studied predominantly in WHO functional class II-III patients.1
PH=pulmonary hypertension.
- Adempas Prescribing Information. Whippany, NJ. Bayer Pharmaceuticals Inc., 2021.
- Humbert M, Kovacs G, Hoeper M, et al. 2022 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension. Eur Heart J. 2022;00:1-114.
- McLaughlin VV, Archer SL, Badesch BD, et al. ACCF/AHA 2009 expert consensus document on pulmonary hypertension: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation Task Force on Expert Consensus Documents and the American Heart Association: developed in collaboration with the American College of Chest Physicians, American Thoracic Society Inc., and the Pulmonary Hypertension Association. Circulation. 2009;119(16):2250-2294.
- Badesch DB, Raskob GE, Elliot CG, et al. Pulmonary arterial hypertension: baseline characteristics from the REVEAL Registry. Chest. 2010;137(2):376-387.
- Hoeper MM, Barberà JA, Channick RN, et al. Diagnosis, assessment, and treatment of non-pulmonary arterial hypertension pulmonary hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;54(1 Suppl):S85-96.
- Simonneau G, Gatzoulis MA, Adatia I, et al. Updated clinical classification of pulmonary hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;62(25 Suppl):D34-D41.










